There are three main types of electric vehicles (EVs), classed by the degree that electricity is used as their energy source. Many combinations such as diesel/electric, gasoline/flywheel, and fuel cell (FC)/battery are usually used. Typically, one energy source is storage and the other converts
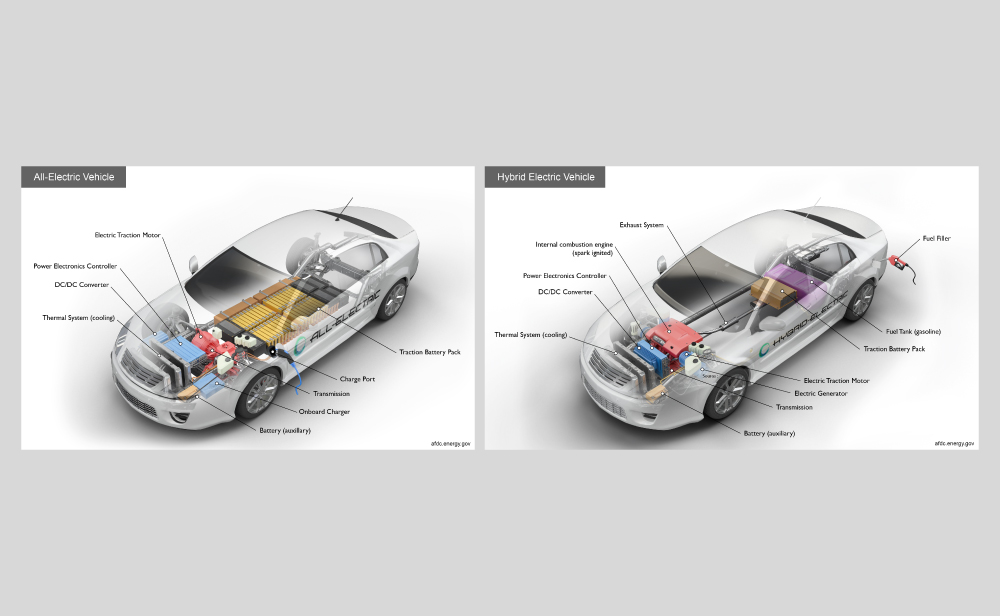
1. Plug-in Electric Vehicle (PEV)– Also called Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs), and more frequently called EVs.This means the car runs purely on electricity and gets all their power when they’re plugged in to charge.Their battery power is used to run the electric motor and all onboard electronics. They don’t need petrol or diesel to run so don’t produce any emissions like traditional cars.
Level 1 charging: 120 V| 8 hours| 75-80 miles
Level 2 charging: 240 V| 4 hours| 75-80 miles
Level 3 charging: 480 V|30 minutes| 90 miles
Pros
- No emissions, hence reducing the carbon footprint
- No gas or oil changes
- Ability to conveniently charge at home
- Fast and smooth acceleration
- Low cost of operation & maintenance
Cons
- Shorter range than gasoline vehicles
- Slightly more expensive in their upfront cost than their gasoline-equivalent although the gasoline savings pay off the difference in typically 2-3 years.
2. Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV)– These mainly run on electricity but also have a traditional fuel engine so you can use petrol or diesel too. If you run out of charge, the car will switch to using fuel. When it’s running on fuel, these cars will produce emissions but when they’re running on electricity, they won’t. Plug-in hybrids can be plugged in to an electricity source to recharge their battery.
3. Hybrid-Electric Vehicle(HEV) – These run mainly on fuel like petrol or diesel but also have an electric battery too, which is recharged through regenerative breaking. These let you switch between using your fuel engine and using ‘EV’ mode at the touch of a button. These cars cannot be plugged in to an electricity source and rely on petrol or diesel for energy.
Pros (PHEV & HEV)
- Longer range than BEV
- Less gas consumption than the gas only vehicle
- Fewer emissions
- Engines tend to be smaller, lighter & more efficient
Cons (PHEV & HEV)
- Produces tailpipe emissions
- Needs gas and oil changes
Which one to choose?
A Plug in Hybrid Electric Vehicle(PHEV) and Hybrid Electric Vehicle(HEV) is a middle ground between a traditional gasoline vehicle and a pure electric vehicle.More preferred when regular longer range commute is required and charging stations are few and located far ahead. A Plug-in Electric Vehicle(PEV) can be preferred when charging stations are at home or located nearby facilitating easy commute within vehicle range.


Leave A Comment