Welcome to the 6th chapter of the knowledge series by Inverted University. In the last chapter, we learned about How does a lithium-ion battery work? , if you are new to this series, we recommend you to do visit the previous chapters.
Solid State Batteries, which store more energy, charge faster, and are safer than liquid lithium-ion batteries, could be a game-changer for electric vehicles (EVs), speeding up the transition away from fossil fuel-powered vehicles.

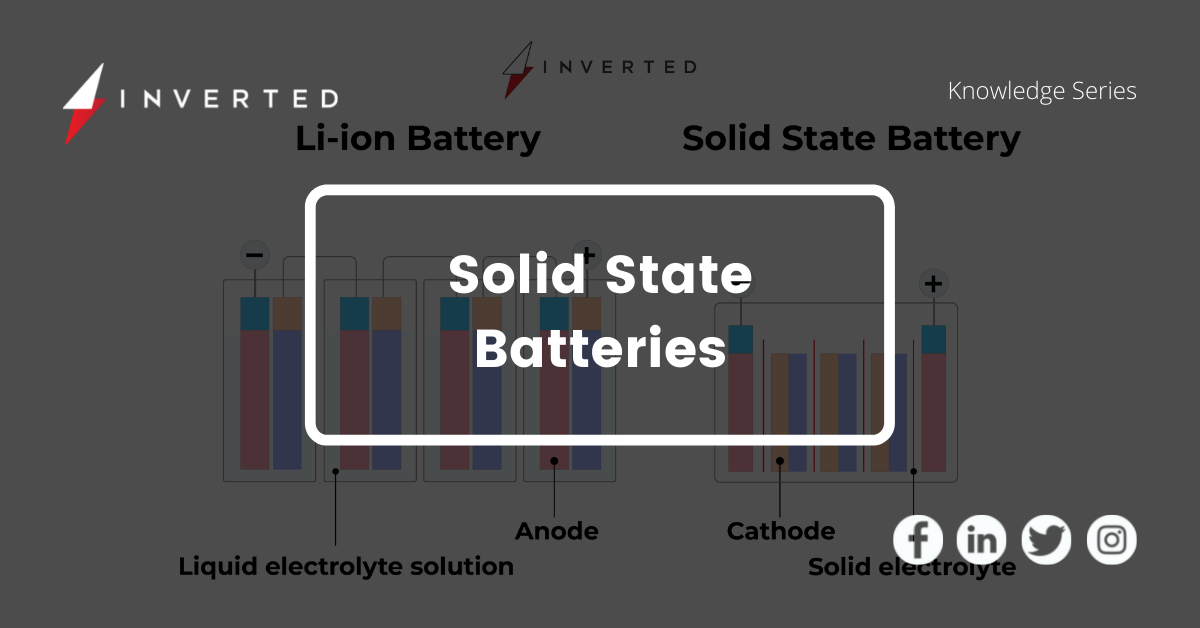
Solid-state batteries are different from Lithium-Ion batteries
Thin layers of solid electrolytes transport lithium ions between electrodes in solid-state batteries, whereas Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries use liquid electrolytes and separators to keep the positive and negative electrodes from coming into contact.
Solid-state batteries are being employed in devices like pacemakers and smartwatches.
Experts estimate that mass-market production of these batteries for electric vehicles will take three to five years.
Why do we need Solid State batteries?
Well if we talk about the purpose of solid-state batteries, it’s to increase the capacity of electric vehicle batteries.
EVs are expected to replace ICEVs (internal combustion engine vehicles) and become the norm in the car industry, according to market research firms. And, to become the undisputed industry leader, EVs must get equal levels of mileage as current ICEVs, which necessitates increasing the battery capacity of an EV battery.
Capacity can be increased by increasing the number of batteries available. However, in this case, the cost of the battery rises, and batteries take up a lot of room in the car.
The energy density of a solid-state battery is higher than that of a Li-ion battery with a liquid electrolyte solution. Because there is no chance of explosion or fire, there is no need for safety components, which saves space. Then we have more room to add more active materials to the battery, increasing its capacity.
Because just a limited number of cells are required, a solid-state battery can maximize energy density per unit area. As a result, a solid-state battery is ideal for constructing a high-capacity EV battery module and pack system.
Advantages
They’ll probably be safer and more stable than liquid Li-ion batteries, which have a volatile electrolyte that can catch fire at high temperatures. As a result, electric vehicles powered by lithium-ion batteries are more susceptible to fires and chemical leaks.
Increased stability means faster charging and fewer bulky safety devices are required.
They can store more energy than liquid li-ion batteries, allowing for a faster transition from gasoline to electric vehicles by reducing the number of times drivers must stop to charge their vehicles.
Barriers in mass production
Carmakers and technology firms have been able to build solid-state lithium-ion battery cells one at a time in the lab, but have yet to scale up to mass production.
It’s difficult to create a stable, chemically inert solid electrolyte that’s also a good ion conductor between the electrodes. They’re costly to make and are prone to cracking because of the brittleness of the electrolytes, which expand and contract during use.
Experts estimate that a solid-state cell costs around eight times more to manufacture than a liquid Li-ion battery.
Global organization working on solid-state batteries
Toyota Motor Corporation of Japan is one of the forerunners in mass-producing solid-state batteries. It has stated that despite their short service life, it aims to begin manufacturing them by the mid-2020s.
Toyota has partnered with Panasonic Corp of Japan to produce these power packs through their Prime Planet Energy & Solutions Inc venture, in addition to its research.
Close behind, Volkswagen has invested in QuantumScape Corp, a Bill Gates-backed U.S. battery company that plans to introduce its battery in 2024 for VW’s EVs and later for other carmakers.
The battery, according to VW, will have around 30% greater range than a liquid battery and will charge to 80% capacity in 12 minutes, which is less than half the time of the quickest charging lithium-ion cells currently available.
Stellantis (STLA.MI), which was founded in January by the merging of Fiat Chrysler and PSA, has a joint venture with TotalEnergies named Automotive Cells Co and cooperation with China’s Contemporary Amperex Technology Co Ltd. By 2026, Stellantis plans to introduce solid-state batteries.
Solid Power, a firm founded by Ford Motor Company (F.N) and BMW AG (BMWG.DE), claims that their solid-state technology can produce 50% more energy density than current lithium-ion batteries. By the middle of the decade, Ford aims to have decreased battery prices by 40%.
Hyundai Motor, which has invested in SolidEnergy Systems, expects to begin commercial production of solid-state batteries around 2030.
Indian company working on Solid-state batteries
Omega Seiki has stated that solid-state battery technology will be introduced in India. The business has teamed up with the C4V of Revolutionary York to bring the new battery technology to the United States.


Leave A Comment